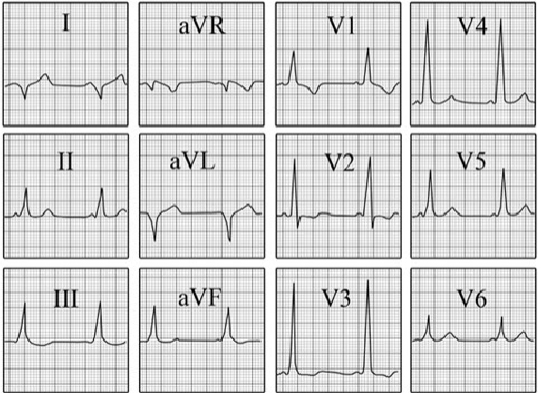
You are incorrect - the best interpretation of the electrocardiogram in our patient is right ventricular hypertrophy and biatrial enlargement.
Click on the links to learn about this ECG:
Your choice: Ventricular pre-excitation
The characteristic features demonstrated here include: a short PR interval .
Delta waves or slurring of the initial portion of the QRS; prolongation of the QRS; and secondary ST-T wave changes.
These findings are the result of an accessory pathway that bypasses the A-V node and produces aberrant activation of the ventricle, as seen in the Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome.
The tall R wave in V1 in this type of Wolff-Parkinson-White is due to posteroanterior activation of the ventricle.